| [1]斐明,曲绵域,于长隆,等.凋亡在骨关节病发病机制中的作用[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19:167-169.[2]Zheng X, Xia C, Chen Z, et al. Requirement of thephosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway for the effect of nicotine on interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat model of osteoarthritis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 423(3):606-612. [3]Ou Y, Tan C, An H, et al. Selective COX-2 inhibitor ameliorates osteoarthritis by repressing apoptosis of chondrocyte. Med Sci Monit.2012;18(6):BR247-52. [4]Kim KM, Kim JM, Yoo YH, et al. Cilostazol induces cellular senescence and confers resistance to etoposide-induced apoptosis in articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2012; 29(4):619-624.[5]Okuma C,Kaketa T,Hikita A,et al.Potential involvement of p53 in ischemia/reperfusion-induced osteonecrosis.J Bone Miner Metab.2008; 26(6):576-585.[6]蓝旭,刘雪梅,葛宝丰,等.β-七叶皂代甙钠对肢体缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2000,9(6):572-573.[7]Karahalil B,Polat S,Senkoylu A,et al.Evaluation of DNA damage after tourniquet-induced ischaemia/reperfusion injury during lower extremity surgery.Injury. 2010;41(7): 758-762.[8]庄洪.川芎嗪对肢体缺血再灌流损伤的临床实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2001,14(6):343-344.[9]Blake DR, Merry P, Unsworth J, et al. Hypoxic-reperfusion injury in the inflamed human joint. Lancet.1989;332(8633): 289-292.[10]Soran N, Altindag O, Cakir H, et al. Assessment of paraoxonase activities in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Redox Rep.2008;13(5):194-198.[11]Mrowicka M, Garncarek P, Bortnik K, et al. Activity of superoxide dismutase (CuZn-SOD) in erythrocytes of patients after hips alloplasty. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008;24(143): 396-398. [12]Altindag O, Erel O, Aksoy N, et al. Increased oxidative stress and its relation with collagen metabolism in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int.2007;27(4):339-344. [13]Iio H, Ake Y, Saegusa Y, et al. The effect of lipid peroxide on osteoblasts and vascular endothelial cells: the possible role of ischemia-reperfusion in the progression of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Kobe J Med Sci.1996;42: 361-373.[14]Schneider T, Drescher W, Becker C,et al. Reperfusion capacity of the femur head after ischemia: an experimental study. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb.1998;136: 132-137.[15]张敬东,陈华,温宏.诱导型一氧化氮合成酶在股骨头骨关节软骨缺血-再灌注后的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(10):1830-1832.[16]Schumer M, Colombel MC, Sawczuk JS,et al.Morphologic, biochemical, and molecular evidence of renal ischemia.Am J Pathol.1992;140: 831-838.[17]Lobb I, Mok A, Lan Z, et al. Supplemental hydrogen sulphide protects transplant kidney function and prolongs recipient survival after prolonged cold ischaemia-reperfusion injury by mitigating renal graft apoptosis and inflammation. BJU Int. 2012; 110(11):E1187-95.[18]Krams SM, Egawa H,Quinn MB,et al.Apoptosis as a mechanism of cell death in liver allograft rejection. Transplantation.1995;59: 621-625.[19]齐丽彤,张钧华,李大元,等.血管紧张素ⅠⅡ型受体阻断剂抑制大鼠缺血-再灌注模型心肌细胞凋亡[J].中华心血管病杂志,2001, 29(2):118-121.[20]Burns AT, Davies DR, Mclaren AJ, et al. Apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion injury of human renal allografts. Transplantation.1998;66: 872-876.[21]Qi Y,Chen L,Zhang L,et al.Crocin prevents retinal ischaemia/reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis in retinal ganglion cells through the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Exp Eye Res.2012; 107C:44-51. [22]Liu DH, Yuan FG, Hu SQ, et al.Endogenous nitric oxide induces activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 via S-nitrosylation in rat hippocampus during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.Neuroscience. 2013; 229:36-48. [23]Gibson G, Lin DL, Roque M. Apoptosis of terminally differentiated chondrocyte in culture. Exp Cell Res.1997;233: 372-382.[24]Hatori M, Klatte KJ, Teixeria CC,et al. End labeling studies on fragmented DNA in the avian growth plate: evidence of apoptosis in terminally differentiated chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Res.1995;10: 1960-1968.[25]Zhao Z,Ji H, Jing R, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy reduces progression of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits byreducing nitric oxide level and chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012;132(11):1547-1553. [26]Lee HG, Yang JH. PCB126 induces apoptosis of chondrocytes via ROS-dependent pathways. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(10):1179-1185. [27]Pokharna HK, Monnier V, Boja B, et al. Lysyl oxide Maillard reaction-mediated crosslinks in aging and osteoarthritic rabbit cartilage. J Orthop Res.1995;13: 13-21.[28]Von der Mark K, Kirsch T, Nerlich A, et al. Type Ⅹ collagen synthesis in human osteoarthritis cartilage: indication of chondrocyte hypertrophy. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35: 806-811.[29]Grskovic I, Kutsch A, Frie C, et al. Depletion of annexin A5, annexin A6, and collagen X causes no gross changes in matrix vesicle-mediated mineralization, but lack of collagen X affects hematopoiesis and the Th1/Th2 response. J Bone Miner Res.2012; 27(11):2399-2412.[30]Tian Y, Peng Z,Gorton D,et al.Immunohistochemical analysis of structural changes in collagen for the assessment of osteoarthritis.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2011; 225(7):680-687. |
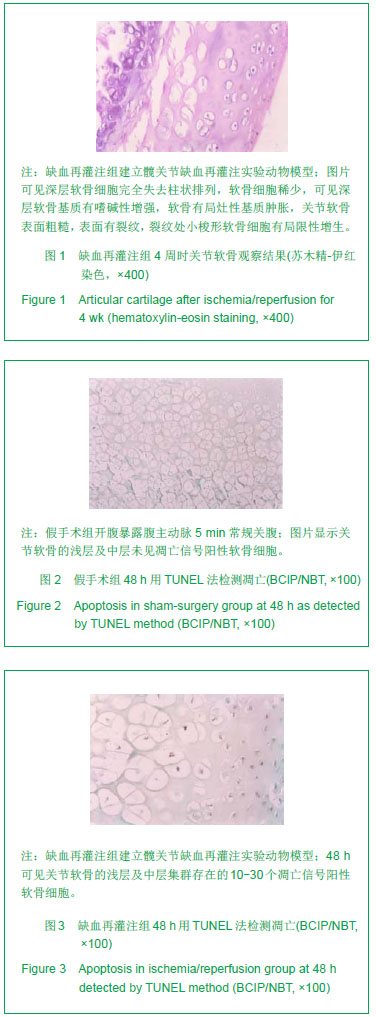
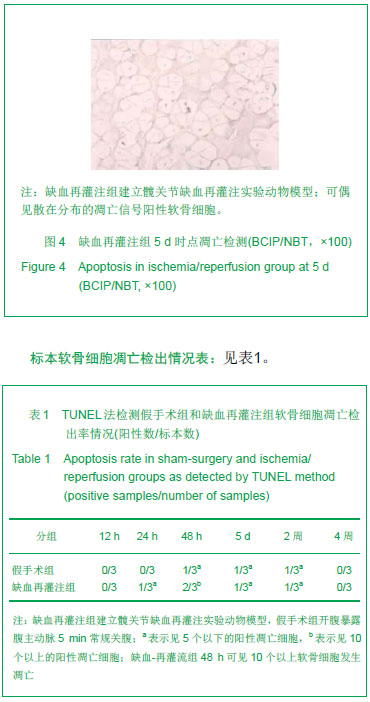
.jpg)